The Difference Between Spin Columns and Centrifuge Tubes
Spin columns and centrifuge tubes are both laboratory consumables used for sample preparation and separation, but they have different purposes and designs. Here are some of the key differences between spin columns and centrifuge tubes:
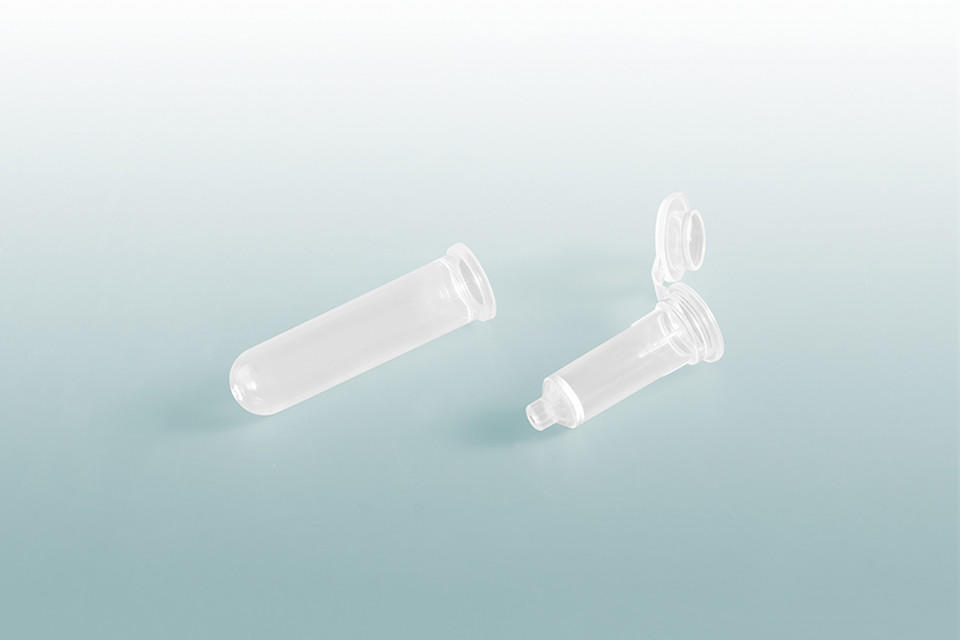
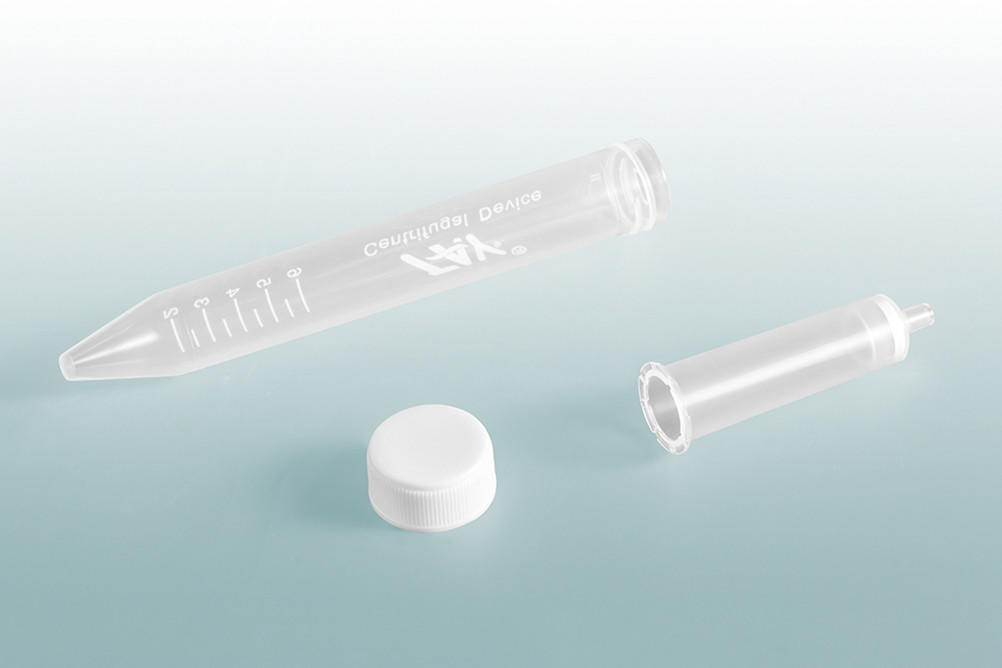
Used for purification and separation of biological molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Consist of a plastic column with a frit at the bottom and a collection tube.
Samples are loaded onto the top of the column, which is placed in a centrifuge to separate the target molecule from impurities.
The purified molecule is collected in the collection tube, while the impurities remain trapped in the column.
Centrifuge Tubes:
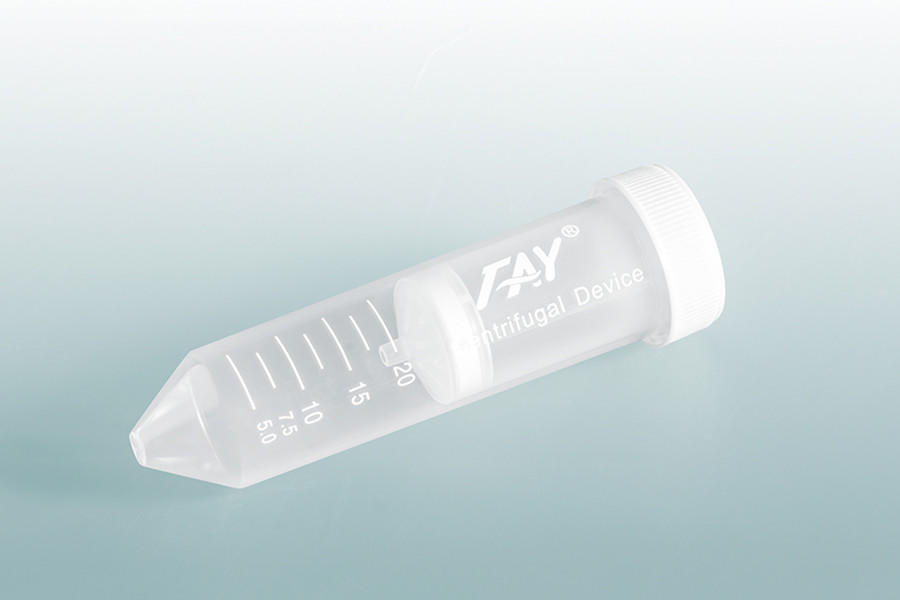
Used for sample preparation, storage, and separation of various materials such as cells, viruses, and proteins.
Consist of a plastic or glass tube with a conical or cylindrical shape and a cap or screw top.
Samples are loaded into the tube and placed in a centrifuge to separate the different components based on their density.
The separated components can then be easily removed or further processed.
Overall, spin columns are more specialized for the purification and separation of biological molecules, while centrifuge tubes are more versatile and can be used for a wider range of applications.
What Is The principle of Centrifuge Tubes?
Centrifuge tubes work based on the principle of centrifugal force, which is the force that causes objects to move away from the center of rotation. When a sample is loaded into a centrifuge tube and spun at high speeds, the different components of the sample will move apart based on their density and size.
The basic principle of centrifuge tubes is that denser particles in the sample will move toward the bottom of the tube, while lighter particles will move toward the top. This is because the centrifugal force generated by the spinning tube creates a gradient of force that is strongest at the bottom of the tube and decreases towards the top.
Centrifuge tubes are typically designed with a conical or cylindrical shape that facilitates the separation of the different components. When the tube is spun in a centrifuge, the denser components will move toward the bottom of the tube, forming a pellet or layer, while the lighter components remain in the upper part of the tube.
Once the separation is complete, the different components can be removed from the tube using a pipette or another extraction method. Centrifuge tubes are commonly used for a variety of applications, including the separation of cells, viruses, proteins, and other biological materials, as well as for sample storage and preparation.

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文