What Is The Purpose of PCR Tubes in Medicine?
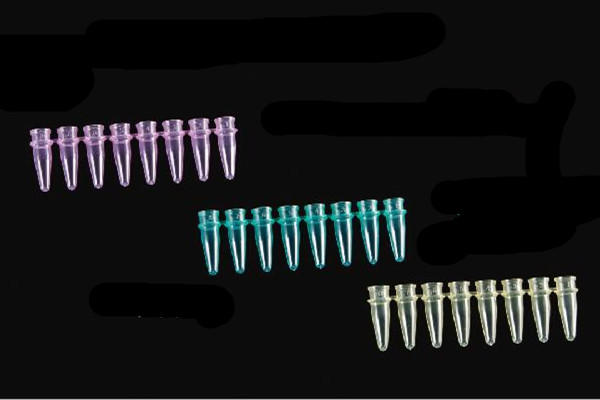
PCR tubes are small plastic tubes used in molecular biology and medical research. PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction, which is a widely used technique for amplifying DNA sequences.
The purpose of PCR tubes in medicine is to enable the amplification of DNA sequences for various diagnostic and research purposes. PCR tubes are used to hold small quantities of reaction mixtures containing the DNA sample, primers, and enzymes needed for the PCR process.
PCR tubes are designed to withstand the high temperatures required for the PCR process, which involves heating and cooling the reaction mixture to specific temperatures to amplify the target DNA sequence. They are typically made of high-quality plastic or other materials that can withstand the extreme temperatures and chemicals used in the PCR process.
PCR tubes are essential tools in molecular biology and medical research, as they allow scientists to amplify and analyze specific DNA sequences with high accuracy and sensitivity. They are widely used in a variety of applications, including genetic testing, diagnosis of infectious diseases, forensics, and drug discovery.
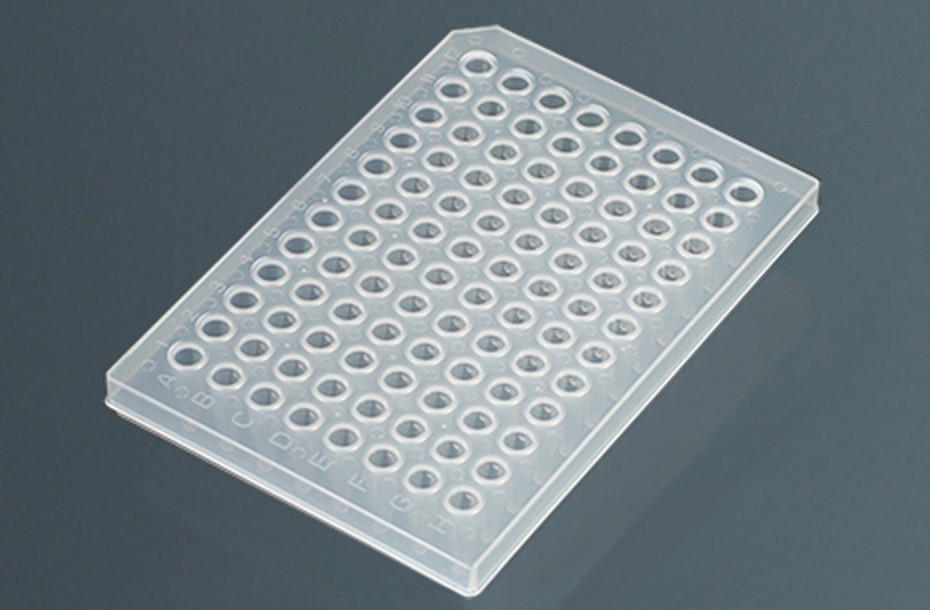
The Emergence of Deep Well Plate
Deep well plates are a type of laboratory consumable used for sample preparation, storage, and analysis. They are typically made of plastic and have a rectangular shape with a series of wells or compartments that can hold liquid samples.
The emergence of deep well plates can be traced back to the mid-20th century, when the need for large-scale sample preparation and analysis in various fields, such as biochemistry and biotechnology, began to increase. At the time, many researchers were using traditional test tubes and flasks to prepare and store their samples, which was a time-consuming and labor-intensive process.
The first deep well plates were introduced in the 1960s as a more efficient alternative to traditional glassware. These early deep well plates had relatively large well volumes, typically around 2-3 mL, and were designed for manual use in laboratories.
In the 1980s, with the advent of high-throughput screening and automated laboratory equipment, the demand for deep well plates increased dramatically. Manufacturers began to produce deep well plates with higher well densities, smaller well volumes, and improved automation compatibility.
Today, deep well plates are widely used in a variety of applications, including sample preparation, storage, and analysis in drug discovery, genomics, proteomics, and other areas of research. They are available in a range of good volumes, from as little as 50 μL to as much as 10 mL or more, and can be used with a variety of automated laboratory equipment, such as liquid handling robots and plate readers.

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文